When we go out to eat, how often do we worry about food poisoning?
You probably shouldn’t worry because HACCP may have you covered. This is a system designed to keep everybody safe so that they can enjoy their dinner out without worrying about falling ill from bad food.
But is your favorite restaurant following it? Are the authorities enforcing it or is it voluntary?
Read on to find out more…
What is HACCP?

HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points. It is an established set of standards for promoting food safety for the public.
It aims at protecting consumers and workers at organizations. Since its introduction more than 50 years ago, food-borne hazards (such as the spread of listeria, monocytogenes, salmonella, shigella, etc) have significantly reduced.
HACCP procedures require players to follow hygienic steps in food preparation, inspecting of raw materials, handling chemicals and raw materials.
It takes a farm-to-dinner table approach, focusing on the whole food chain from production, conditioning, packaging, and distribution, to retail and food establishment.
The idea is to contain hazards before they can happen—whether in the form of biological, chemical, or physical threats. It also fights threats like food fraud and adulteration.
By helping to build a safer environment, this program reassures consumers about safety.
Who established and administers it?
HCCAP was established in the 1960s by 3 entities partnering together: NASA, the US Army Laboratories, and the Pillsbury Company.
Its mission was to establish a control system for making food safe for astronauts traveling to space.
However, HACCP isn’t a government agency. It is simply a system for food safety management.
In the US, HACCP is administered by the Food Safety Inspection Service (FSIS) under USDA.
The HACCP is continuously reviewed or updated to ensure that it stays responsive to situations, especially when new cases of food poisoning break out.
The plan places responsibility on both employers and employees. For example, employers are expected to ensure food hygiene training in their outlets. Their employees are also expected to be familiar with the HACCP process.
HACCP: Voluntary or Mandatory Process?

HACCP is a voluntary process. It is mostly up to individual food outlets to follow or adopt.
Unlike previous food safety systems, it puts more responsibility on food processors to implement them. This includes the development, implementation, and success of the HACCP system.
Despite being voluntary, HACCP is highly recommended for managing food safety. For example, the FDA guidelines on HACCP state that it “endorses the voluntary implementation of food safety management systems in retail and foodservice establishments.”
It calls for food operators to work with their regulatory authorities and health inspectors to ensure safe food through systems like HACCP.
However, these guidelines also state that the ultimate responsibility for food safety lies with the food operators.
The guidelines state that the HACCP can be integrated with the business operations such that it makes food safe just as routine as other elements in the business like opening in the morning or managing cash flow.
Mandatory Aspects
Some specialized food processes are subject by law to HACCP plans. These include curing and smoking food.
It also includes reduced oxygen packaging of foods. For these processes, food and hospitality outlets are legally required to obtain HACCP plans and variances.
Foods serving areas or kitchens are required by law to have a HACCP plan.
So, while HACCP is not a government program, food regulatory bodies like the FDA may require it.
International recognition for HACCP standards

The HACCP system is internationally recognized and has become a global standard for benchmarking food processing organizations.
For example, ISO 22000, is an ISO standard specifically for food that incorporates HACCP.
Through this, an organization can get ISO certified by proving compliance with HACCP.
However, HACCP can also be applied independently of ISO 22000 or other management system standards.
Through the Codex Alimentarius Commission, the World Health Organization (WHO) has also officially defined and recognized the HACCP.
Some countries have taken specific actions relating to HACCP either making it voluntary or mandatory;
- United States: The US has a regulatory requirement for the meat and poultry sector that embraces HACCP. Also, under US Seafood Regulation, HACCP is mandatory for all seafood exporters to the US.
- The European Union: Although it is not mandatory to have a fully-fledged HACCP system, the EU Regulation No 852/2004 has food safety regulations based on HACCP principles. It states: “Food business operators shall put in place, implement and maintain a permanent procedure based on the Codex HACCP principles.”
- China: Despite China being a leading international meat producer, few of its production processes are HACCP certified. The momentum toward adoption of HACCP however is increasing. For example, the Chinese government has a China HACCP program.
HACCP core principles
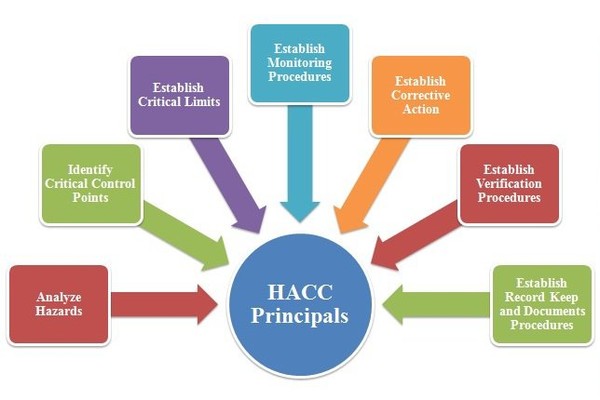
The food safety management system by HACCP has 7 principles:
- Performing hazard analysis
- Establishing CCP or Critical Control Points
- Installing a control and monitoring system for the CCP
- Setting critical limits
- Taking corrective actions
- Requiring confirmation steps to ensure the effectiveness of the system
- Record keeping and documentation
Outbreaks where HACCP has helped or could help
Food poisoning scares in public have occurred before which proves the need for HACCP plans. Some examples are:
- The jack-in-the-Box outbreak in 1993
- The Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (mad cow disease) outbreak
- The more recent COVID-19 global outbreak where it is suspected that bats from wet food markets in Wuhan, China was the source of the virus
Many of these outbreaks could have been prevented by better tracking and handling. HACCP preventive measures are just what would be needed in such cases.
In the US, an assessment found there was a 7-year reduction of 20% in food-borne diseases by following HACCP rules.
Although there is no guarantee that HACCP plans can eliminate the hazards, they can significantly reduce their seriousness and help to prevent them from occurring or spreading far.
Challenges to HAACP adoption

If HACCP is beneficial, why aren’t some voluntarily adopting it?
Other than the lack of enforcement some barriers to adopting HACCP have been identified. This is largely affecting developing countries.
- Cost of equipment
- Lack of clarification by authorities
- Lack of information
- Lack of training and education
- Absence of surveillance program
Solutions to overcoming some of these barriers include providing training courses that increase the knowledge and expertise of managers and employees in the food processing industries.
Gains from Volunteering in the HACCP process
- It can help you avoid costly litigation by affected customers
- It helps you to secure profits and sales
- It gives your staff training for the Code of Federal Regulations for Meat and Poultry HACCP (9CFR417)
- More efficiency in food handling among your staff
- Long term savings
- Strong brand value and customer loyalty
By gaining HACCP certification, it’s easier to showcase your business to customers and let them know that you are taking their health and safety seriously.
Conclusion
Even though it is not mandatory, there is everything to gain from adopting HACCP plans.
Many outlets are already proud participants in it on a voluntary basis.
As noted, it’s a smart strategic business move as it could help you edge out your competition and enhance your reputation in the eyes of customers.

