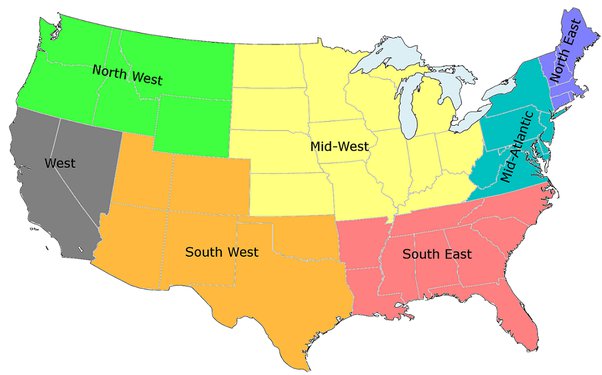
How can we best classify places that share similar characteristics?
No doubt the most familiar one is through nationalities or areas enclosed by national or political boundaries.
But geographers have gone beyond this to use cultural regions that can be quite powerful at getting deeper insights into a people’s identity, sense of place, and connection with their geography.
Cultural regions may overlap and therefore do not necessarily conform to political boundaries.
What Is A Cultural Region?
A cultural region is a concept used in geography to refer to an area that is identifiable by a common cultural trait or set of human activities.
Such factors may include customs, religion, cuisine, political system, or activity in trade.
Cultural regions, also known as cultural areas or cultural spheres are very important to geographers as they simplify a complex world and make geographers see the interconnections between different places.
Types of Cultural Regions
There are 3 types of cultural regions:
A. Functional regions
Functional regions are easily mapped areas because they have well-defined boundaries. They are organized around a certain function that may be political, social, or economic.
They typically feature a nodal point that can be national capitals, industrial centers, parish churches, city halls, banks, or factories.
A functional region can lie across political boundaries, for example, a drainage system that belongs to a big river that connects more than one state.
Crossing the boundaries of functional regions can also lead to a change of rules.
This signifies you are in a different functional region. For example, state lines that divide different states make you enter different jurisdictions or states that have different rules.
Or you can have a pizza franchise e.g. Pizza Hut that has boundaries and rules. You may not be able to order from a pizza franchise located in a particular functional region unless you are located within it.
B. Formal Regions
Formal regions are more difficult to map as they have fuzzy boundaries or less well-defined boundaries.
They usually have two main parts: a core and a peripheral area.
The core or central part exhibits more of the common trait that distinguishes a formal region.
As you move outward from the core, you enter the peripheral or outer parts of the formal region.
The trait diminishes as you move more and more away from the core into the peripheral areas.
Finally, you reach the end where the trait vanishes and you are outside the region.
Characteristics of a formal region can be either related to humans or physical geography.
For example, ethnicity, language, climate, or vegetation are all traits that can define a formal region.
See examples here: 15+ Formal Region Examples
C. Vernacular Regions
Vernacular regions are the least well-defined cultural regions compared to the others. This is because they are usually imaginary and therefore can vary with individuals.
Since they depend on perception, they are also called perceptual regions.
These perceptions are held by people who may be living either in or outside the regions.
Despite their ill-defined nature, vernacular regions are important because people believe in them.
Different people choose different variables to define it so it’s hard to pinpoint specific locations like its core or periphery.
See examples here: 15 Vernacular Region Examples
Cultural Region Examples
Here are 10 examples of cultural regions:
1. Latin America
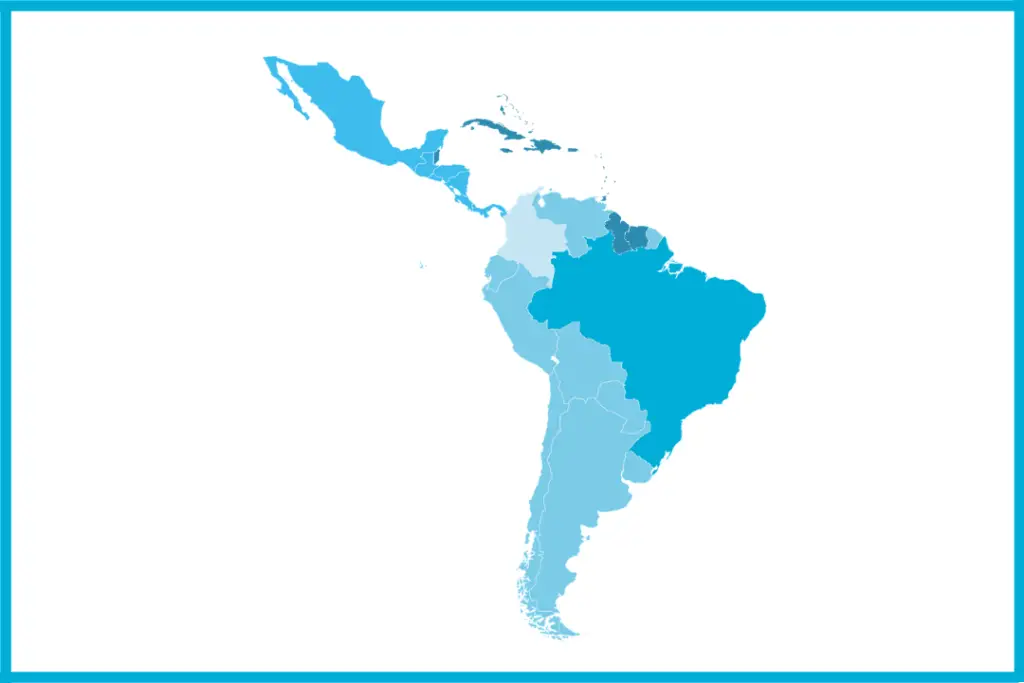
This area is a formal area that comprises all the territory that falls south of the US.
It derives its term, Latin from its previous colonization by Portugal and Spain.
Both Portugal and Spain spoke Latin as a language.
The religion practiced is predominantly Christian of the Roman Catholic faith.
Also, the main languages spoken are Portuguese and Spanish (known as Romance languages).
The dominant race is mixed people of European and Native American Indian descent.
So, the characteristics that distinguish the Latin American region are language, religion, and common historical background.
2. Chinatown
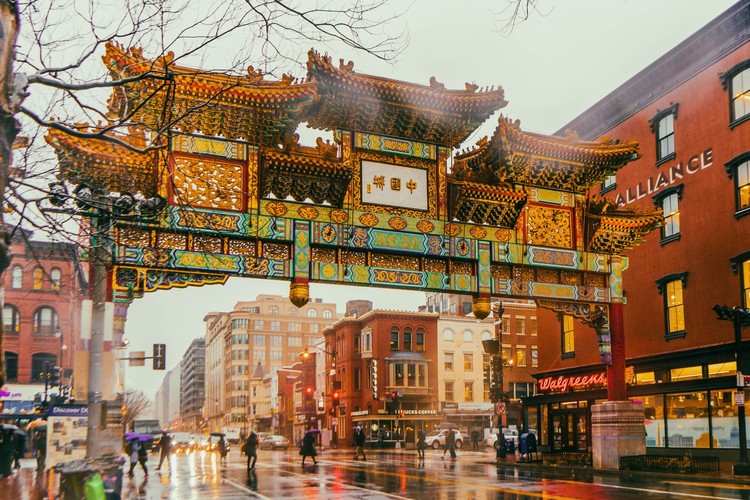

These are cultural regions found all over the world including North America, South America, Europe, Africa, and Australia.
They are districts or enclaves in non-Asian towns (i.e. located in urban areas outside of Taiwan, mainland China, etc.).
They are typically dominated by the Chinese language or Chinese ethnic group.
In the US, Chinatowns are located in cities such as San Francisco or Los Angeles.
New York Metropolitan area has the highest Chinese populated area outside Asia.
Chinatowns are not always associated with China or Chinese languages. Some would more accurately be called Little India or Koreatown. For example, the AsiaTown in Cleveland, Ohio.
In Africa, Chinatowns are found Mauritius and Madagascar with the largest being in South Africa.
3. Dixie
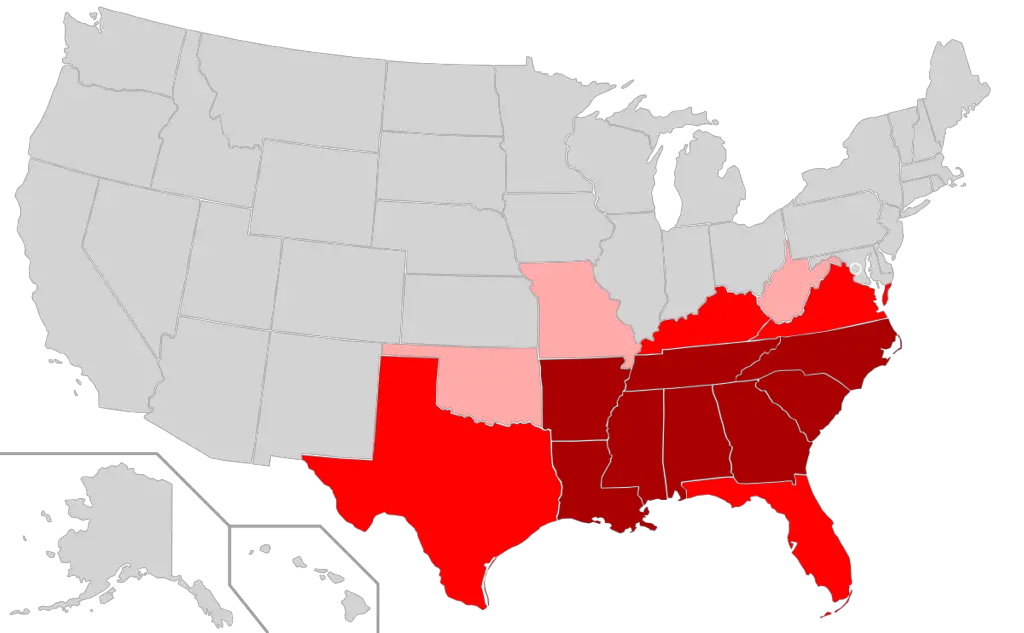
Dixie is a vernacular region that is used to refer to the American South.
However, since different people apply different variables to define the south, you can’t tell which specific states, towns or counties are parts of Dixie.
Though a definite boundary is lacking for it, most people define Dixie as the states that fall below the Mason-Dixon line. It also includes the Deep South.
Dixie also has a shared history of states that seceded from the North and which formerly belonged to the Confederacy.
The name Dixie stirs nostalgic memories of the south during the 20th century which was expressed in a song.
4. Metropolitan Areas

Metropolitan areas consist of several cities, towns, or suburbs.
It has a major city that functions as the hub or core as most of the activity such as commerce or traffic occurs there. It is also densely populated.
Examples of metropolitan areas include Chicago, Dallas, Philadelphia, Washington DC, and Los Angeles.
The largest metro area in the US is the New York metropolitan area. Its core is New York City which serves a number of vital functions such as a location for the stock exchange.
Its sprawl spans regions in 4 states: New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Connecticut, and New York.
5. Anglo-America

This is an area in North America whose principal spoken language is English.
It also shares historical ties with Northern Europe along with its customs and folklore.
Most of the US and English-speaking Canada (i.e. excluding Quebec which is French speaking) are included.
It can be distinguished from Latin America which is Spanish speaking. Its population is also predominantly white in race.
6. Corn Belt
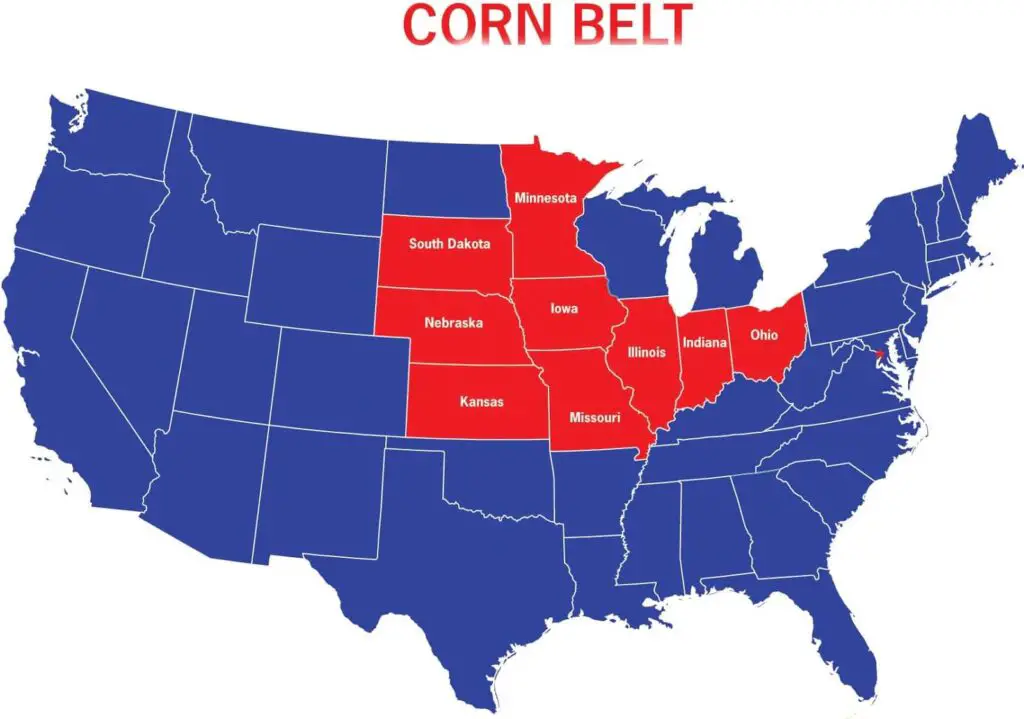
The Corn Belt is an area known for growing corn.
It’s a formal area with its core located in Iowa where corn growing is highly concentrated and is called corn king.
As you move outward and reach places like Pennsylvania, less corn is grown, which shows you are outside the Corn Belt.
The region is made up of about 12 states, including western Indiana, eastern Kansas, Missouri, and Iowa.
This region is the highest producer of corn in America, so corn growing helps to distinguish it as a cultural region.
7. Bible Belt
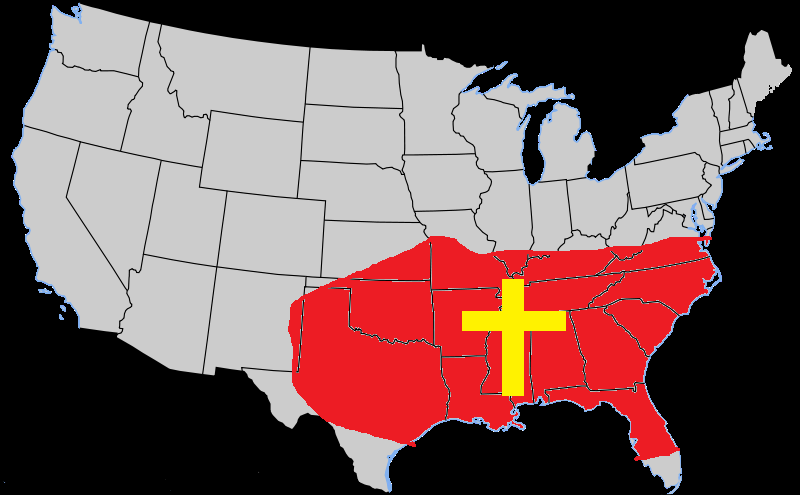
This region in the US is characterized by a strong evangelical Christian presence.
The Christian evangelical faith has a strong cultural influence on the region. This includes devotion and adherence to biblical teachings and having the highest church attendance in the US.
However, as a vernacular region, the Bible Belt does not have any universally agreed boundaries. So one can’t tell where it starts and ends.
8. Mormon Area or Corridor
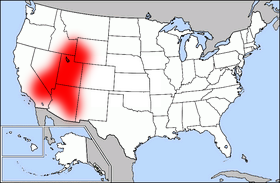
Salt Lake City, which is situated in the state of Utah, has a very large population of the LSD (Latter Saints Day) Church, which makes it the node of a formal region of the Mormon culture.
Therefore, Utah is considered a cultural area with Salt Lake City as its node. As you move outwards, the Mormon population decreases.
The Mormon Corridor has also been styled as the Jell-O belt because of the popularity and high consumption of Jell-O by inhabitants.
Some of its distinctive cultural practices include an emphasis on family and larger-than-average families, all influences of religious doctrines of the LSD.
9. the State of Texas
The state of Texas is a cultural region with distinct characteristics across it like shared historical experiences and a way of life that Texans are proud of.
Texas also has some areas in it that can be considered cultural regions such as Hill Country, Gulf Coast, or Panhandle.
These have unique landscapes and traditions. For example, the Gulf Coast is densely populated and has a humid warm climate. However, Big Bend country is dry.
10. Slavic Europe
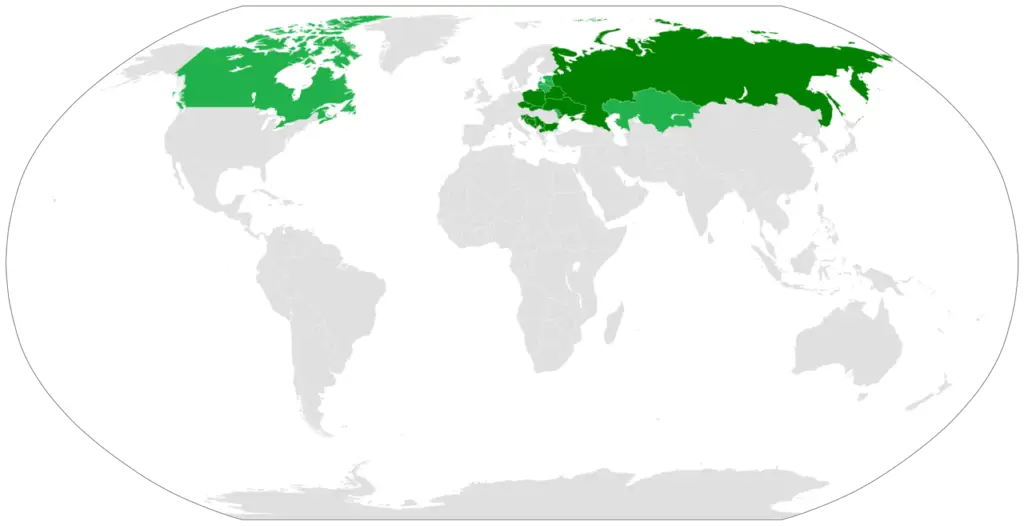
This is a cultural region that is located in northern Eurasia consisting mainly of Eastern and Central Europe with Siberia in the east and the Balkans found in the west.
Its main attribute is its Slavs people. Their main common trait is the speaking of Slavic languages.
Slavs also have a large Diaspora in the US due to immigration.
Some major classifications of these people are Russians, Poles, Slovaks, Serbs, and Czechs.
Conclusion
Rob a biologist of the cell or a physicist of the atom and you have deprived them of the vital tool of their trade.
The geographer will be faced with the same predicament if you deny him the cultural region.
It is the basic unit of analysis for geographers to understand a diverse world.