DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) has been described as the molecule of life.
It has been found in the cells of all organisms that have ever been observed. But is it possible that we could have organisms with no DNA?
So far, the organisms we know are just a fraction of all living organisms. Many more organisms are still unknown.
Clues from the organisms we already know about suggest that perhaps there could be DNA-lacking organisms that are yet to be discovered.
Keep in mind that organisms can be either single-celled (such as bacteria or yeast) or multicellular (such as humans).
If we found an organism with no DNA, it would have to be single-celled.
Why Cells need DNA
For both single-celled organisms and multicellular organisms, DNA is crucial for survival and function. This is because DNA has the instruction code for constructing proteins in cells.
Proteins are needed to run almost every process in living things. Therefore, most cells would be useless without DNA.
For example, each of the following is a characteristic of life. Each requires the activity of DNA and the proteins it produces in order to work in cells.
- Metabolism and respiration
- Growth and change
- Sensitivity to the environment
- Replication and passing off traits to new cells
- Continuity of life
From this, we would conclude that it is unthinkable for a cell to have no DNA. But there must be exceptions. Let’s explore…
The question of whether all cells have DNA can be approached at two levels:
- Single-celled organisms: Do all single-celled organisms have DNA?
- Multicellular organisms: Do all the cells in multicellular organisms have DNA?
Cells with no DNA in multicellular organisms
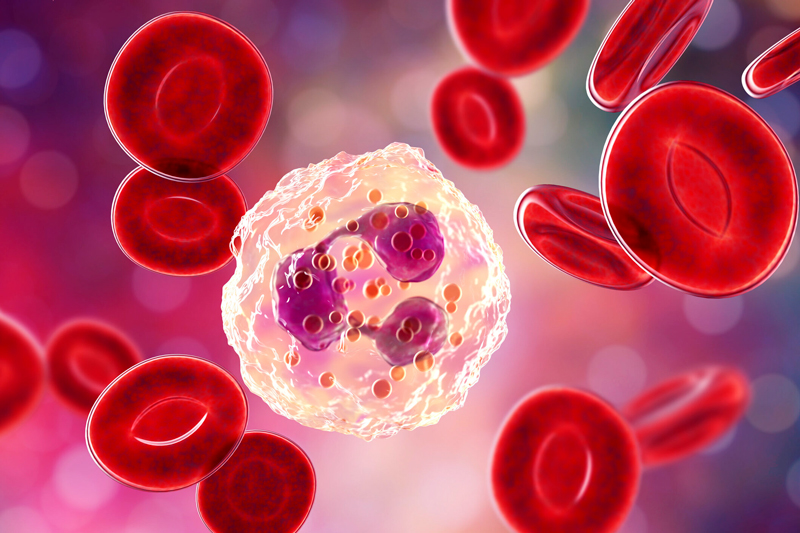
Some cells found in multicellular organisms don’t have a nucleus in them. These are called anucleated cells.
This means they do not have DNA since all eukaryotic DNA needs to be enclosed in the protective enclosures in the form of a nucleus.
Examples:
A. Blood cells
These include erythrocytes (red blood cells) and platelets in humans or mammals.
These cells initially start off with a nucleus but in their maturing process, they get rid of their nucleus in order to maximize their oxygen-carrying capacity.
The DNA and nucleus are required in the initial stages since it has the instruction code for the cell’s development.
Once the cell has developed, DNA is not required anymore so it is discarded.
However, red blood cells with no nucleus are only found in mammals.
B. Cornified cells
Found in the skin, hair, and nails, these also have no nucleus or DNA.
Like red blood cells, they also destroy their nucleus when they mature.
These cells need to maximize packing space for keratin, a structural protein that gives structural strength. For this reason, they discard their nucleus when they are mature.
C. Sieve tubes (in phloem)
These are the structures that plants use to conduct food.
Despite sacrificing their nucleus, these cells still rely on other cells that have a nucleus. For example, red blood cells need the bone marrow cells to be generated as new blood cells.
Therefore, they cannot exist independently without cells that have a nucleus.
Viruses that lack DNA
Viruses can have either DNA or RNA. However, viruses are not considered to be cells, organisms, or indeed living things.
Instead, they are thought of as fragments or particles that carry nucleic acid (DNA or RNA).
They do not perform basic life metabolic processes like cellular respiration, photosynthesis, or fermentation.
However, they do perform reproduction but only by hijacking cells to use their DNA.
RNA world vs the DNA world
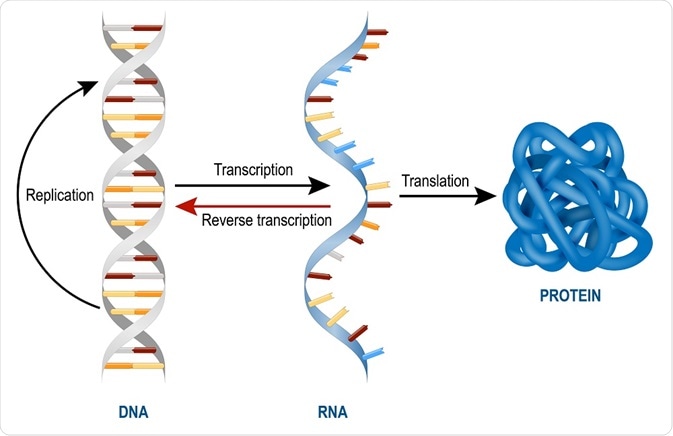
Carl Woese, Francis Crick, and Leislie Orgel came up with the RNA World Hypothesis.
In it, they theorize the first life that emerged on earth had RNA as its genetic material instead of DNA.
RNA is a very unstable molecule which makes it less efficient for storing genetic information compared to DNA.
Therefore, over time, organisms evolved more efficient systems in which RNA was replaced by DNA. This is the reason why virtually all modern species have DNA as their main hereditary molecule.
But how were the first organisms able to function without DNA considering that cells need DNA to produce life-essential proteins? The answer could lie in a groundbreaking discovery that scientists made about a previously unknown function of RNA.
A group of scientists led by Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech won the 1989 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for discovering ribozymes.
Ribozymes are RNAs that are able to both function as genes and proteins (perform chemical reactions like enzymes).
So, RNA could have fulfilled the role of both DNA and proteins when neither had yet to be formed. This lends support to the RNA world theory in which cells with no DNA existed.
Final Verdict
Finding an organism today with no DNA would be like chancing on a needle on a haystack. This search, much like the relentless search for alien life continues.
The only cells lacking DNA appear to be specific cells in multicellular organisms that exist together with other cells that have DNA.
Related post: What is The Purpose of Detergent in DNA Extraction?

