In your high school science classes, you probably got introduced to osmosis. So, it may sound a bit confusing to hear about reverse osmosis!
Let’s refresh a bit on your high school osmosis lesson and then dash back to take a look at reverse osmosis to understand it.
Osmosis is defined as a process where water molecules (or other solvent molecules) in a solution move from high to low concentrations areas through a semi-permeable membrane.
So, the characters in this scene are the solvent (water), the solute (ions such as salt or sugar), the solution (dissolved mixture), and a semipermeable membrane (a barrier that allows selective diffusion).
Osmosis is a passive process with no requirement for any energy input. The water seeks equilibrium (equal concentration) between both sides of the partition.
We can already see this in cell transport where the cell membrane acts as a semi-permeable membrane.
If that’s osmosis, think of it in the reverse direction! In other words, water molecules move from low to high concentration areas through the semipermeable membrane.
How can this happen and why would we want that?
Osmosis is a process that takes place naturally, so it just happens. However, reverse osmosis isn’t a natural process, so something has to be done (by us humans!) to persuade it to happen. This calls for technology.
The Process of Reverse Osmosis
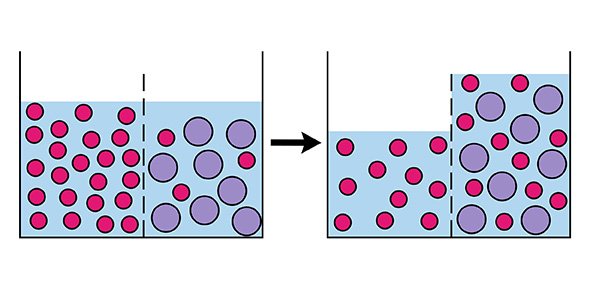
Imagine if we have a saltwater solution and pure water separated from each other in a tank by a semipermeable membrane.
To push the side with saltwater through the membrane to the other side, we need to apply pressure.
However, since salt molecules are bigger than water molecules, only the water molecules will pass through.
This leaves the saltwater side even more concentrated but the pure side with more pure water.
In this way, we have achieved reverse osmosis! This is the basis for many applications including water purification.
Here are 6 reverse osmosis examples in real life.
1. Desalination

We have come a long way since the days scientists first attempted to desalinate ocean water in the 1950s.
The amounts of freshwater they produced were too little to be of use.
However, using cellular acetate as a membrane, the process is now faster and efficient.
Large desalination plants are now used in more than 100 countries to produce vast amounts of fresh drinkable water from salty seawater.
2. Preventing fluoridation diseases
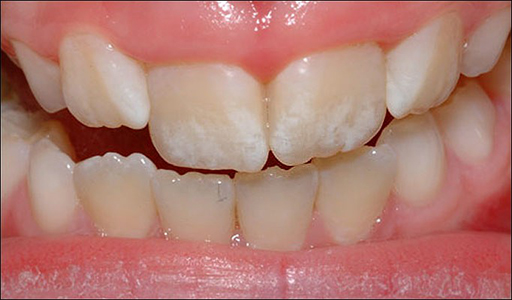
Water can sometimes have very high levels of fluoridation. That leads to a condition called enamel fluorosis when we drink the water.
Another condition called skeletal fluorosis makes your bones bend and lose their strength.
Nothing works better than reverse osmosis to get out the fluoride at a large scale.
3. Dialysis

When kidney patients reach the final stage of kidney disease which is called kidney failure, their kidneys can’t function anymore and death can occur within minutes due to toxin buildup in the blood.
Unless patients can get a new kidney via transplant, the only option is dialysis.
Dialysis is the cleansing of your blood by using an artificial kidney or dialyzer.
Dialysis uses reverse osmosis to ensure that the water used is of the purest form with no contamination. This reduces the chances of infection or disease which can be dangerous.
4. Water for Injection (WFI)

Most medicines get absorbed through your digestive system, so all you need is to swallow them by mouth.
However, other medicines have to be administered through a different route such as intravenous or direct injection into your body. This gives a faster absorption and also a quicker and stronger effect of the drug.
Medicines are usually prepared as solutions but using ordinary water such as tap or bottled water for the medicine solutions is dangerous. They may contain bacteria that may cause septicemia when they get into the bloodstream.
By using reverse osmosis, pure water (WFI) with no contamination can be obtained for safer medicine administration.
Also Check: 11 Concentration Gradient Examples in Real Life
5. Concentrating milk

Milk has a huge water content of about 87 percent.
So, imagine trying to transport large quantities of such milk or its products over long distances. The shipping costs can soar due to the space required.
With reverse osmosis, those costs can be cut done dramatically. This is done by concentrating the milk which removes the water but retains the solid part.
Farmers can benefit from this technology by using less tank space for milk cooling, lower hauling costs, and greater profit.
6. Maple Syrup

Maple syrup is considered to be a healthier alternative to refined sugar. It has been used as a sweetener for centuries.
But to get the maple syrup, you have to separate it from it the water by boiling the sap.
This evaporates away the water to leave behind the concentrate of maple syrup.
However, the boiling time can be quite long.
Using reverse osmosis, however, we can reduce the water amount in the sap before boiling.
This can dramatically reduce the boiling time by up to 70 percent making the process more efficient.
Conclusion
Pressure isn’t something we always like. But when it comes to reverse osmosis, we better like pressure!
With our planet running short of fresh water, it’s our best shot to generate vast amounts of freshwater even from the dirtiest or most putrid water.